VFT Extended DApp Frontend Integration Guide
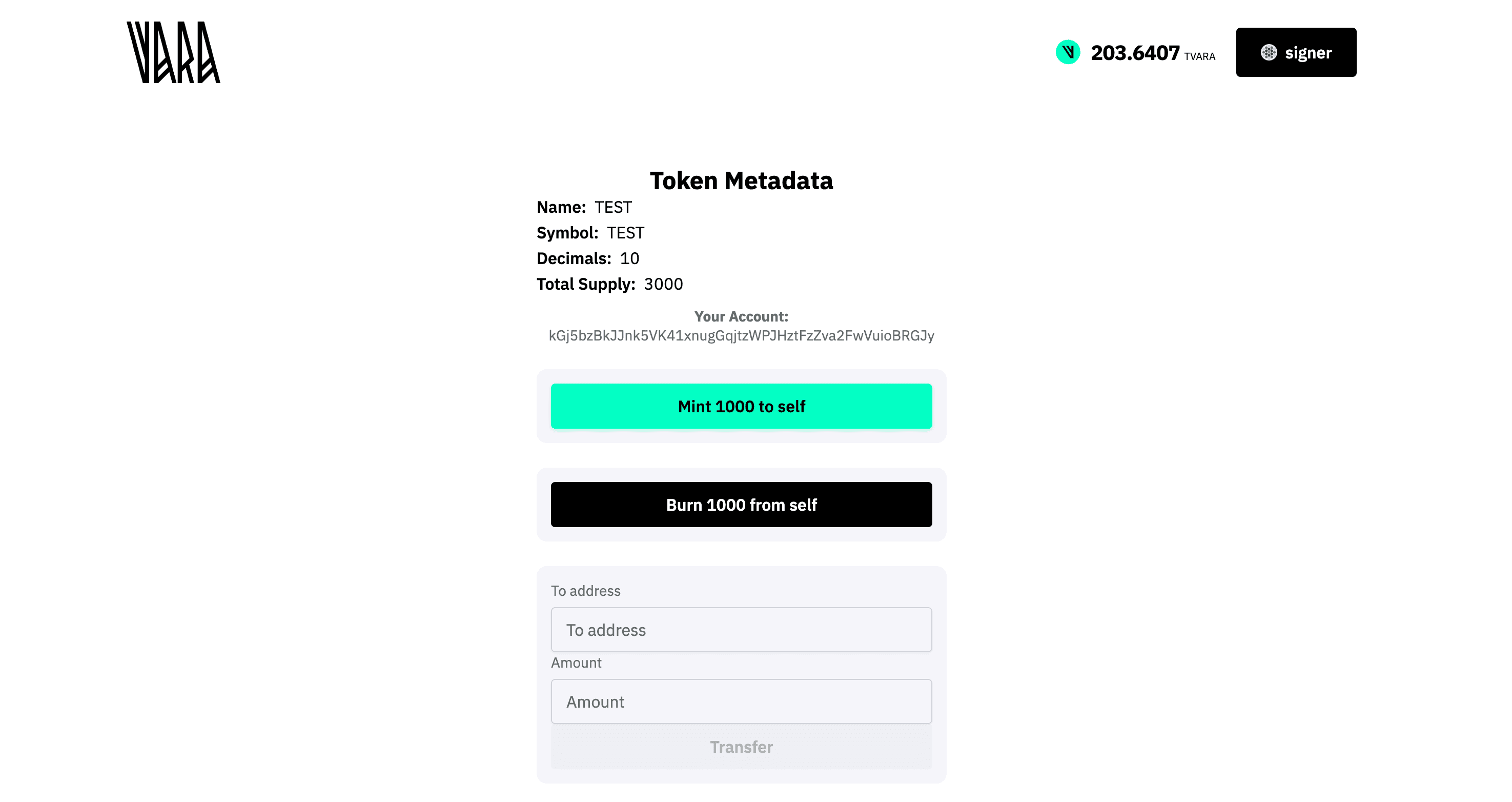
This guide explains how to build a frontend application in React that interacts with the VFT Extended (Vara Fungible Token) contract, using sails-js React hooks. The document provides a step-by-step approach, code samples, and configuration tips for quickly integrating contract calls, queries, and event listeners.
Who is this for?
- React developers integrating smart contract features into a DApp on the Vara blockchain.
- Anyone needing a working example and best practices for
sails-js hookswith VFT contracts.
You will learn:
- How to set up a project from a template
- How to generate a contract TypeScript client interface
- How to implement and use hooks for transactions, queries, and events
- How to build UI components for interacting with the VFT contract
Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure your environment is ready:
- Node.js (version 18+ recommended)
- Yarn or npm
- Git
- Gear IDEA (for contract deployment, not needed for frontend only)
- Access to Vara network (e.g., testnet node, test tokens to make transactions)
- Installed browser wallet (e.g., Polkadot.js extension or compatible with Substrate network)
- Basic knowledge of React, TypeScript, and smart contract architecture
Prerequisites
Before starting the frontend development, ensure your contract is uploaded to the Vara Network and you have its Program ID ready.
Interaction with the network is impossible without a deployed contract.
Project Setup
Create Frontend App from Template
Use the official Vara React app template. Run in your terminal:
npx degit gear-foundation/dapps/frontend/templates/create-vara-app dApp
cd dApp
yarn install # or npm install
yarn start # or npm startTemplate Features
The provided template is production-ready and includes:
- Wallet Connection: Pre-configured interaction with Vara-compatible wallets.
- Node Provider: Pre-set connection to the Vara Network.
- Alert System: Built-in notifications for user feedback.
- Contract Ready: Fully prepared for smart contract integration.
Project Structure Overview
After setup, important files and folders are:
.env # Environment variables (node, contract addresses)
src/consts.ts # App-level constants from env
src/hooks/ # Your custom and generated React hooks
src/components/ # UI components
src/App.tsx # Main app entryGenerating TypeScript Client (lib.ts) for Your Contract
Deploy Your Contract
Make sure your VFT contract is already deployed on Vara testnet or mainnet (via Gear IDEA) and you have its address (ProgramId).
Generate Client Library
Follow the client generation instructions: Client Generation Docs
npx @gear-js/sails codegen --program <YOUR_PROGRAM_ID> --output src/hooks/lib.ts--programis your deployed contract ID (0x...).--outputis the path for generated TS client code.
Add Library to Hooks
Import the generated client (ABI) in your hooks, e.g.:
import { SailsProgram } from './lib';Type-Safe API Access
The generated file (IDL) provides a full description of your contract's API.
Use it to enable type-safety on the frontend, ensuring that your calls match the contract's expected arguments and return types.
Environment Configuration
Create a .env file in the project root:
VITE_NODE_ADDRESS=wss://testnet.vara.network
VITE_CONTRACT=0x... # your deployed contract addressAdd a config file (consts.ts) for environment variables:
export const ENV = {
NODE: import.meta.env.VITE_NODE_ADDRESS as string,
CONTRACT: import.meta.env.VITE_CONTRACT as `0x${string}`,
};Implementing React Hooks for Contract Interaction
Additional Resources
For detailed documentation on Sails React Hooks and up-to-date API examples, check out these links:
Your hooks (e.g., hooks/api.ts) wrap all main contract actions, queries, and event subscriptions.
Program Instance
import { useProgram } from '@gear-js/react-hooks';
import { SailsProgram } from './lib';
import { ENV } from '../consts';
export function useProgramInstance() {
return useProgram({
library: SailsProgram,
id: ENV.CONTRACT,
});
}Token Actions (Mint, Burn, Transfer)
import { useSendProgramTransaction } from '@gear-js/react-hooks';
export function useSendMintTransaction() {
const { data: program } = useProgramInstance();
return useSendProgramTransaction({
program,
serviceName: 'vft',
functionName: 'mint',
});
}
export function useSendBurnTransaction() {
const { data: program } = useProgramInstance();
return useSendProgramTransaction({
program,
serviceName: 'vft',
functionName: 'burn',
});
}
export function useSendTransferTransaction() {
const { data: program } = useProgramInstance();
return useSendProgramTransaction({
program,
serviceName: 'vft',
functionName: 'transfer',
});
}Token Queries
import { useProgramQuery } from '@gear-js/react-hooks';
export function useTokenQueries() {
const { data: program } = useProgramInstance();
const { data: name, isPending: isNamePending } = useProgramQuery({
program, serviceName: 'vft', functionName: 'name', args: [],
});
// ... (symbol, decimals, totalSupply)
return { name, /* ...other fields */ };
}API Reference
For a full list of query methods and detailed usage, see the React Hooks API Reference.
Query with Parameters
export function useBalanceOfQuery(address: `0x${string}`) {
const { data: program } = useProgramInstance();
return useProgramQuery({
program,
serviceName: 'vft',
functionName: 'balanceOf',
args: [address],
watch: false,
});
}When to use watch?
The watch parameter determines how frequently your data updates:
- Use
watch: true: For dynamic data like balances or values affected by frequent user actions and contract events. - Skip
watch: For static data such as token names, symbols, or decimals to improve app performance.
Listen to Events
import { useProgramEvent } from '@gear-js/react-hooks';
export function useTokenEvents(callbacks) {
const { data: program } = useProgramInstance();
useProgramEvent({
program,
serviceName: 'vft',
functionName: 'subscribeToMintedEvent',
onData: (data) => callbacks.onMinted?.(data),
});
// ... subscribe to burned, transferred, approval
}Full Implementation Example
For a complete, production-ready example of the hooks setup, refer to the source code: hooks/api.ts on GitHub
Making Transactions
const { sendTransactionAsync: sendMint, isPending: mintPending } = useSendMintTransaction();
const { sendTransactionAsync: sendBurn, isPending: burnPending } = useSendBurnTransaction();
const { sendTransactionAsync: sendTransfer, isPending: transferPending } = useSendTransferTransaction();
await sendMint({ args: [toAddress, amount] });
await sendBurn({ args: [fromAddress, amount] });
await sendTransfer({ args: [toAddress, amount] });Handle UI loading states and errors:
if (mintPending) { /* show spinner */ }
try {
await sendMint({ args: [account.decodedAddress, '1000'] });
// show success
} catch (e) {
// show error
}Making Queries
Use useTokenQueries() and useBalanceOfQuery() to read contract state:
const { name, symbol, decimals, totalSupply, isLoading } = useTokenQueries();
const balanceQuery = useBalanceOfQuery(someAddress);
if (balanceQuery.isPending) { /* loading */ }
else { /* show balanceQuery.data */ }Listening to Contract Events
Another way to keep your frontend application in sync with the blockchain is by listening to contract events.
When the contract emits events (e.g., on mint, burn, transfer), you can subscribe to them in your React code and automatically react to changes — for example, to refresh balances or update state.
Unlike the watch option in queries (which polls data on every block), event listeners let your app respond immediately when something of interest happens in the contract, without unnecessary polling.
Subscribe to contract events and trigger UI updates:
useTokenEvents({
onMinted: () => refetchTotalSupply?.(),
onBurned: () => refetchTotalSupply?.(),
// onTransfer, onApproval...
});This ensures real-time UI updates after mint/burn operations.
UI Example: Home Component
A minimal example of how to use the new transaction hooks and queries in a component:
import { useAccount, useAlert } from '@gear-js/react-hooks';
import { useState } from 'react';
import {
useSendMintTransaction,
useSendBurnTransaction,
useSendTransferTransaction,
useTokenQueries,
useTokenEvents,
useBalanceOfQuery,
} from '../../hooks';
function Home() {
const { account } = useAccount();
const { name, symbol, decimals, totalSupply, isLoading, refetchTotalSupply } = useTokenQueries();
const alert = useAlert();
const [transferTo, setTransferTo] = useState('');
const [transferValue, setTransferValue] = useState('');
const [balanceAddr, setBalanceAddr] = useState('');
const { sendTransactionAsync: sendMint, isPending: mintPending } = useSendMintTransaction();
const { sendTransactionAsync: sendBurn, isPending: burnPending } = useSendBurnTransaction();
const { sendTransactionAsync: sendTransfer, isPending: transferPending } = useSendTransferTransaction();
useTokenEvents({
onMinted: (data) => alert.info(`Mint event: ${JSON.stringify(data)}`),
onBurned: (data) => alert.info(`Burn event: ${JSON.stringify(data)}`),
});
// ...handlers for mint, burn, transfer, balance
// ...render UI with all actions, inputs, loading states, errors
}
export { Home };For the full and up-to-date example, see Home.tsx on GitHub
For Vara UI Kit component details and usage, see
vara-ui on GitHub.
Notes and Best Practices
- Handle async errors to improve UX.
- Use event subscriptions to keep UI state in sync with blockchain.
- For production: review security, error boundaries, and consider adding better wallet management and notifications.
Security First
Never hard-code private keys or sensitive data in the frontend.
Always use environment variables (.env) for node endpoints and contract addresses to keep your application secure and configurable.